Lungs Cancer
Lung cancer is one of the most prevalent and deadly forms of cancer worldwide. It’s a complex disease with numerous variables affecting its progression, treatment, and outcomes. Understanding the nuances of lung cancer, from symptoms to survival rates, can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of lung cancer, including its symptoms, signs, survival rates, and treatments, with a focus on small cell carcinoma and the unique symptoms observed in females.
Understanding Lung Cancer
What is Lung Cancer?
Lung cancer begins in the lungs, two spongy organs in the chest that take in oxygen when you inhale and release carbon dioxide when you exhale. It occurs when cells in the lung mutate and grow uncontrollably, forming a tumor. This tumor can interfere with breathing and spread to other parts of the body.
lung cancer symptoms
signs of lung cancer
lung cancer survival rate
lung cancer treatment
small cell carcinoma
symptoms of lung cancer in females
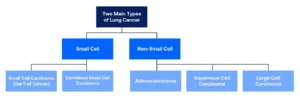
Types of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is primarily categorized into two main types:
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
NSCLC is the most common type, accounting for about 85% of all lung cancer cases. It includes subtypes like adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma. NSCLC generally grows and spreads more slowly compared to small cell lung cancer.
Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC)
SCLC is less common but more aggressive. It tends to grow rapidly and spread quickly to other parts of the body. It is strongly associated with smoking and often diagnosed at an advanced stage.
Symptoms and Signs of Lung Cancer
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of lung cancer early can lead to earlier diagnosis and better outcomes.
General Symptoms
General symptoms of lung cancer can be quite subtle initially and may include:
- Persistent cough that doesn’t go away
- Chest pain that worsens with deep breathing, coughing, or laughing
- Hoarseness
- Weight loss and loss of appetite
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue or feeling weak
- Recurring infections like bronchitis or pneumonia
Early Signs
Early signs of lung cancer often mimic those of less serious conditions, which can make early diagnosis challenging. These signs include:
- A new cough that doesn’t go away
- Changes in a chronic cough or “smoker’s cough”
- Coughing up blood, even a small amount
- Wheezing
Advanced Symptoms
As lung cancer progresses, symptoms may become more severe and noticeable:
- Bone pain (like pain in the back or hips)
- Neurological changes (such as headache, weakness or numbness of a limb, dizziness, balance problems, or seizures)
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Lumps near the surface of the body due to swollen lymph nodes
Symptoms in Females
Lung cancer symptoms in females can sometimes present differently, possibly leading to delays in diagnosis. Women are more likely to experience:
- Non-respiratory symptoms such as fatigue and back or shoulder pain
- Symptoms often attributed to other conditions like menopause or arthritis
Diagnosing Lung Cancer
Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment of lung cancer.
Medical History and Physical Exam
A thorough medical history and physical examination are the first steps in diagnosing lung cancer. Doctors look for risk factors like smoking history, exposure to carcinogens, and family history of cancer.
lung cancer symptoms
signs of lung cancer
lung cancer survival rate
lung cancer treatment
small cell carcinoma
symptoms of lung cancer in females
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests are vital tools in diagnosing lung cancer:
- Chest X-ray: Often the first imaging test used, which can show masses or nodules.
- CT Scan: Provides detailed cross-sectional images of the lungs and can identify smaller lesions that might not be visible on an X-ray.
- PET Scan: Helps to determine if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
Biopsies and Lab Tests
To confirm a lung cancer diagnosis, a biopsy is usually required. Types of biopsies include:
- Bronchoscopy: A flexible tube passed down the throat to collect tissue from the lungs.
- Needle Biopsy: A needle is inserted through the chest wall to obtain lung tissue.
- Sputum Cytology: Examining mucus coughed up from the lungs for cancer cells.
Lung Cancer Staging
Staging determines the extent of cancer and helps in planning treatment and predicting prognosis.
Stages of NSCLC
NSCLC is staged from I to IV:
- Stage I: Cancer is confined to the lungs.
- Stage II: Cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage III: Cancer has spread to lymph nodes in the middle of the chest.
- Stage IV: Cancer has spread to both lungs, fluid around the lungs, or other parts of the body.
Stages of SCLC
SCLC is typically classified as:
- Limited Stage: Cancer is confined to one side of the chest and nearby lymph nodes.
- Extensive Stage: Cancer has spread to other regions of the chest or beyond.
Survival Rates
Survival rates for lung cancer vary significantly based on several factors.
Factors Affecting Survival Rates
Survival rates are influenced by:
- Stage at Diagnosis: Early-stage lung cancer has a higher survival rate.
- Overall Health: Patients in better health may have better outcomes.
- Treatment Response: How well a patient responds to treatment.
Survival Rates by Stage
According to statistics, the five-year survival rates are:
- Stage I NSCLC: Approximately 68-92%
- Stage II NSCLC: Around 53-60%
- Stage III NSCLC: About 13-36%
- Stage IV NSCLC: Approximately 10%
- Limited Stage SCLC: Around 20-30%
- Extensive Stage SCLC: Less than 1%
Treatment Options
There are various treatment options available for lung cancer, depending on the type and stage.
Surgery
Surgery aims to remove the cancerous tissue and may involve:
- Lobectomy: Removing an entire lobe of the lung.
- Pneumonectomy: Removing an entire lung.
- Segmentectomy or Wedge Resection: Removing part of a lobe.
lung cancer symptoms
signs of lung cancer
lung cancer survival rate
lung cancer treatment
small cell carcinoma
symptoms of lung cancer in females
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. It can be used alone or in combination with other treatments, especially if surgery isn’t an option.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing. It can be administered orally or intravenously and is often used in conjunction with surgery or radiation.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy uses drugs that target specific genetic changes in cancer cells. This treatment is particularly effective for certain mutations found in NSCLC.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy helps the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells. It has shown promising results, especially in advanced stages of lung cancer.
Living with Lung Cancer
Living with lung cancer involves managing symptoms and maintaining quality of life.
Coping Strategies
Effective coping strategies include:
- Staying Informed: Understanding the disease and treatment options.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking.
- Mental Health: Seeking support from counselors, support groups, or loved ones.
Support Resources
Numerous resources are available to support lung cancer patients:
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who have similar experiences.
- Counseling Services: Professional help to deal with emotional challenges.
- Patient Advocacy Groups: Organizations providing information, resources, and support.
Conclusion
Lung cancer is a formidable disease, but understanding its symptoms, diagnosis, staging, survival rates, and treatment options can significantly impact outcomes. With advancements in medical research and treatment, patients have more options and hope than ever before. Early detection and proactive management are key to improving survival rates and quality