Brain Hemorrhage
Brain hemorrhages, also known as brain bleeds or hemorrhagic strokes, are serious medical conditions that require immediate attention. These occur when an artery in the brain bursts, causing localized bleeding in the surrounding tissues. This bleeding kills brain cells and can lead to severe health complications. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for brain hemorrhages is crucial for prompt and effective medical intervention.
What is a Brain Hemorrhage?
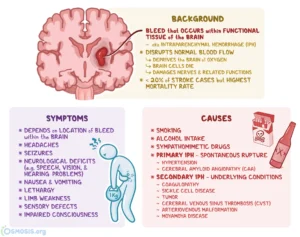
A brain hemorrhage refers to bleeding in or around the brain. It is a type of stroke known as a hemorrhagic stroke. There are several types of brain hemorrhages, including intracerebral hemorrhage, which occurs when the bleeding is within the brain itself, and subarachnoid hemorrhage, which involves bleeding in the area between the brain and the tissues covering it.
hemorrhagic stroke
brain bleed symptoms
brain bleed
hemorrhagic stroke treatment
brain bleed from fall
small bleed on the brain symptoms
intracerebral hemorrhage treatments
brain hemorrhage symptoms
brain bleed treatment
Common Causes of Brain Hemorrhages
Several factors can lead to a brain hemorrhage, including:
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Chronic high blood pressure can weaken blood vessel walls, making them more susceptible to rupture.
- Trauma: Head injuries, such as those sustained in a fall, can cause brain bleeds.
- Aneurysms: These are bulges in blood vessels that can burst and lead to bleeding in the brain.
- Blood Vessel Abnormalities: Conditions such as arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) can disrupt normal blood flow and lead to bleeding.
- Blood Disorders: Conditions like hemophilia and sickle cell anemia can increase the risk of brain hemorrhage.
- Liver Disease: This can cause clotting issues, leading to an increased risk of bleeding.
- Brain Tumors: In rare cases, brain tumors can cause bleeding.
Recognizing Brain Bleed Symptoms
Side effects of a cerebrum drain can shift contingent upon the area and seriousness of the drain. Common symptoms include:
- Sudden, Severe Headache: Often described as the worst headache ever experienced.
- Nausea and Vomiting
- Weakness or Numbness: Particularly on one side of the body.
- Trouble Talking or Grasping Discourse
- Vision Issues
- Loss of Balance or Coordination
- Seizures
- Loss of Consciousness
In cases of a small bleed on the brain, symptoms might be less severe but still require medical attention. These can include mild headaches, slight weakness, or sensory changes.
Immediate Steps to Take
If you suspect someone is experiencing a brain hemorrhage, it’s critical to seek emergency medical help immediately. Early conclusion and treatment can fundamentally further develop results.
Hemorrhagic Stroke Treatment Options
Treatment for hemorrhagic strokes focuses on stopping the bleeding, relieving pressure on the brain, and addressing the underlying cause. Options include:
- Medications: To control blood pressure, prevent seizures, and manage pain.
- Surgical Intervention: In severe cases, surgery may be needed to remove the accumulated blood and repair damaged blood vessels. Procedures such as craniotomy or stereotactic aspiration may be performed.
- Endovascular Procedures: Minimally invasive techniques like coiling or clipping can treat aneurysms or AVMs.
- Rehabilitation: Post-treatment, patients often require rehabilitation to recover lost functions, including physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy.
Intracerebral Hemorrhage Treatments
Specific treatments for intracerebral hemorrhage, where bleeding occurs within the brain tissue, include:
- Emergency Measures: Rapid reduction of blood pressure and control of bleeding.
- Surgical Options: Decompression surgery to alleviate pressure, and minimally invasive techniques to remove the hematoma.
- Ongoing Care: Continuous monitoring and supportive care to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Preventing Brain Hemorrhages
While not all brain hemorrhages can be prevented, certain measures can reduce risk:
- Manage Blood Pressure: Regular monitoring and medication adherence can help control high blood pressure.
- Safety Measures: Using helmets and seat belts can reduce the risk of head injuries.
- Healthy Lifestyle: A balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking can improve overall vascular health.
- Regular Check-ups: Monitoring for conditions like aneurysms or AVMs, especially if there is a family history.
Conclusion
A brain hemorrhage is a life-threatening condition that necessitates immediate medical intervention. Understanding the symptoms and seeking prompt treatment can significantly improve the chances of recovery. With advances in medical treatments and ongoing research, outcomes for patients with brain hemorrhages continue to improve, emphasizing the importance of awareness and proactive healthcare.



